GrassmannCalculus`
GrassmannExpand (★ℰ) |
|
| | ||||
|
| | ||||
|
| | ||||
Details and Options
Examples
(2)
Basic Examples
(1)
In[1]:=
<<GrassmannCalculus`
The inbuilt Mathematica function Expand expands ordinary (Times) products, but not any of the Grassmann products.
In[2]:=
★A;Expand[{(a+b)(c+d),(a+b)⋀(c+d)}]
Out[2]=
{ac+bc+ad+bd,(a+b)⋀(c+d)}
GrassmannExpand
In[3]:=
GrassmannExpand[{(a+b)(c+d),(a+b)⋀(c+d)}]
Out[3]=
{(a+b)(c+d),a⋀c+a⋀d+b⋀c+b⋀d}
GrassmannExpand
In[4]:=
GrassmannExpand[]
ax+by+(c+d)z
Out[4]=
ax
by
(c+d)z
You can also include transformation functions for GrassmannExpand to apply before the expansion. Here the Clifford product is replaced, preventing its expansion. Show Precedence.
In[5]:=
★P |
★★P |
Out[5]=
((x+y)⋀(u+v))⊖((x+y)⋄(u+v))
Out[5]=
(x⋀u)⊖(f[x+y,u+v])+(x⋀v)⊖(f[x+y,u+v])+(y⋀u)⊖(f[x+y,u+v])+(y⋀v)⊖(f[x+y,u+v])
Out[5]=
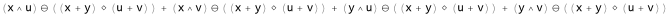
GrassmannExpand will also expand the numerator and denominator of a quotient. Here we have the exterior product of two vectors both in the numerator and denominator.
In[6]:=
★ℬ |
2
★ |
a
★ |
b
★ |
c
★ |
d
★ℰ |
Out[6]=
(+)⋀(+)
a
1
e
1
a
2
e
2
b
1
e
1
b
2
e
2
(+)⋀(+)
c
1
e
1
c
2
e
2
d
1
e
1
d
2
e
2
Out[6]=
()⋀()+()⋀()+()⋀()+()⋀()
a
1
e
1
b
1
e
1
a
1
e
1
b
2
e
2
a
2
e
2
b
1
e
1
a
2
e
2
b
2
e
2
()⋀()+()⋀()+()⋀()+()⋀()
c
1
e
1
d
1
e
1
c
1
e
1
d
2
e
2
c
2
e
2
d
1
e
1
c
2
e
2
d
2
e
2
Simplifying gives their scalar ratio.
In[7]:=
Simplify
[Q]
★ |
Out[7]=
a
2
b
1
a
1
b
2
c
2
d
1
c
1
d
2
In[8]:=
Clear[et,Q]
Properties & Relations
(1)
|
|
""


