The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
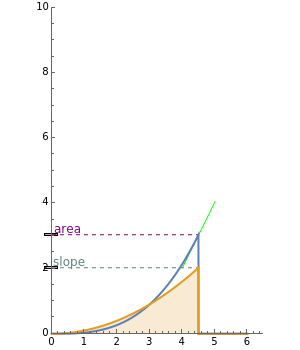
If is a continuous function on and is an antiderivative for on , then f(t)t=F(b)-F(a). If we take and for convenience, then is the area under the graph of from to and is the derivative (slope) of . In the image above, the purple curve is —you have three choices—and the blue curve is .
f
[a,b]
F
f
[a,b]
b
∫
a
a=0
F(a)=0
F(x)
f
0
x
f(x)
F(x)
f(x)
F(x)