Stationary States in a Nonisothermal Continuous Stirred-Tank Reactor
Stationary States in a Nonisothermal Continuous Stirred-Tank Reactor
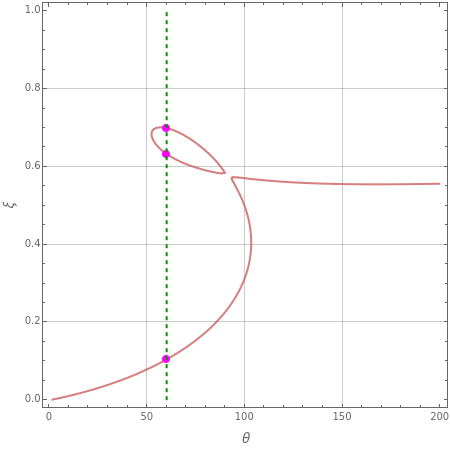
This Demonstration analyzes the single-step reaction in a nonisothermal continuous well-stirred tank reactor (CSTR) where is the heat of reaction. The rate of reaction is first order in the concentration of species , so that , and the rate constant has an Arrhenius temperature dependence: . Heat is removed from the reactor using a cooling coil that has an overall heat transfer coefficient and surface area . The Demonstration shows the complex steady states (expressed as plots of temperature versus , and conversion fraction versus ) that can occur in the reactor as the residence time and the heat transfer parameter are varied. The possibilities include a unique steady state and multiple steady states, as well as the birth and death of an isola (or island), which is a region in the solution space described by a closed loop.
AB+Δ
H
rxn
Δ
H
rxn
A
r=k(T)
C
A
k(T)=exp--
k
m
1
T
1
T
m
T
θ
ξ
θ
θ
=/V
You can study the dynamics of the reactor by varying the initial temperature for the reactor . When multiple steady states are present, each stable steady state will have a zone of attraction that you can explore by changing
T(0)=
T
in
T
in.