Optimal Induction of Foreign Protein Synthesis
Optimal Induction of Foreign Protein Synthesis
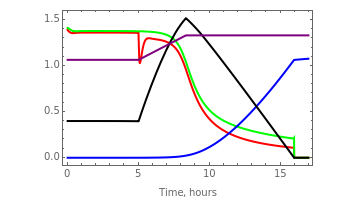
This Demonstration lets you find the best combination of initial conditions and induction parameters to maximize the intracellular accumulation of foreign protein in fed-batch culture of recombinant bacteria. By varying the induction parameters, such as the value of the protein expression rate constant, , before and after induction time and feed rate, you can optimize the foreign protein production at the end of fed-batch culture when the reactor volume reaches its maximum capacity of 100 liters and the residual glucose concentration drops to zero. You can also vary the initial culture volume and initial glucose concentration and segregation probability to further maximize the foreign protein production. The initial concentrations of plasmid-containing cells, , and plasmid-free cells, (as a ratio of the plasmid-containing cells), as well as the segregation probability of generation of plasmid-free cells during the growth of plasmid-containing cells, can also be changed via their sliders, and their effect on the exponential growth curves is shown in the "cell growth" plot.
k
6
+
X
-
X