Mass Transfer in Binary Star Systems
Mass Transfer in Binary Star Systems
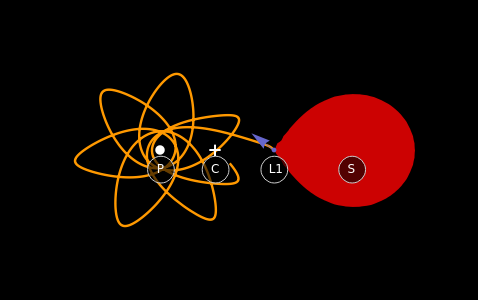
This Demonstration shows the path of a gas particle transferred from a secondary star (S) to a more massive primary star (P) in a binary star system. The gas particle starts at the first Lagrange point (L1). The mass ratio is the ratio of the masses S to P. The initial velocity is shown as a blue arrow and the center of mass (C) is at the point marked +.
If the gas particle is impeded by something such as an accretion disk, then its velocity must change to match the slower velocity gas in the disk. The energy lost during the impact shows as a bright spot on the edge of the accretion disk. Observing such bright spots can provide important information, such as the radius of the disk, which is not directly observable.