Krugman's Model of Increasing Returns and Monopolistic Competition
Krugman's Model of Increasing Returns and Monopolistic Competition
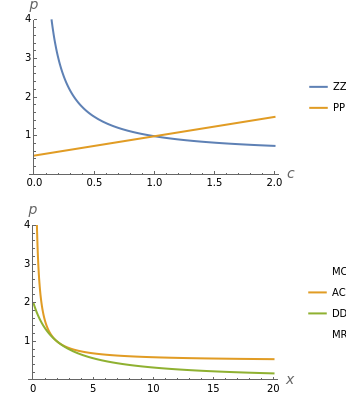
This Demonstration considers Krugman's model of increasing returns and monopolistic competition. Krugman's model can be applied to international trade or the economics of agglomerations. Originally, Krugman considered equilibrium in terms of the relationship between price and consumption (upper plot). This Demonstration adds the more familiar inverse demand representation (bottom plot), which shows the relationship between price and the production quantity . Notice that the typical output of a firm and the typical consumption by an individual have the following dependence: , where is the whole population (total labor)—that is, the main parameter of the model.
p
c
p
x
x=cL
L
All curve labels are constructed as follows: for marginal revenues, for marginal costs, for average cost and for demand (inverse). and are notations used by Krugman [1, pp. 474], where the first reflects and the second shows derived from the Amoroso–Robinson formula. These two curves have no special interpretation in theory, but merely demonstrate the relation of and in the model. That is why it is instructive to bridge the model with a more conventional visualization of monopolistic competition.
MR
MC
AC
DD
ZZ
PP
p/w=β+α/(Lc)
p/w=β(1-ϵ)/ϵ
c
L