Electrical Impedance of Biological Tissues
Electrical Impedance of Biological Tissues
Electrical impedance (or simply impedance or total resistance) measures opposition to a sinusoidal alternating current (AC). Electrical impedance extends the concept of resistance to AC circuits. Impedance is the complex generalization of resistance. In most cases, impedance is a function of the frequency (ω in radians/sec or in hertz), resistance (in ohms), inductance (in henries), and capacitance (in farads):
Z
f
R
L
C
Z=+
2
R
2
(-)
X
L
X
C
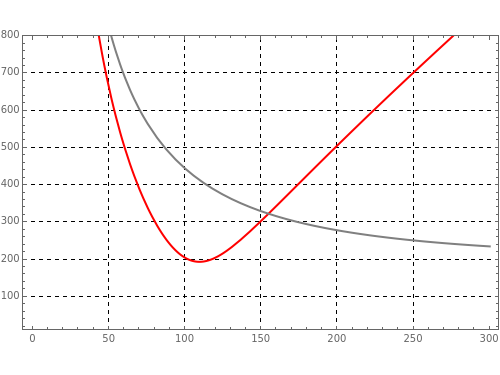
The reactance - is the imaginary part of the impedance, =ωL; =1/(ωC). We consider the impedance to be a function of frequency only; and are constant parameters. The impedance over a range of excitation frequencies is plotted. In the case of biological tissues, the impedance is .
X
L
X
C
X
L
X
C
L
C
Z=+
2
R
2
X
C
The plots show the impedance (total resistance) in red, the biological tissue impedance in gray, and the capacitance resistance in green.
Z
C