Coverage in Fuzzy Subset Relations
Coverage in Fuzzy Subset Relations
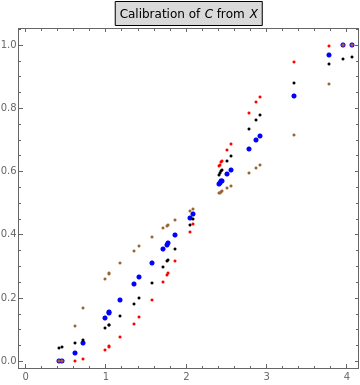
Fuzzy-set qualitative comparative analysis (fsQCA) is a relatively new method used in the social sciences to analyze whether a set of causal conditions () is necessary (), sufficient (), or both necessary and sufficient () for an outcome () to occur. These subset-theoretic relations are assessed on the basis of consistency () and coverage (). The left graphic shows how four popular membership functions assign fuzzy condition set membership scores to 30 cases from a normally distributed base variable (). This assignment is based on the location of the crossover anchor (), which defines the point of maximum set membership ambiguity at 0.5. Functions include the linear function , the quadratic function , the root function , and the logistic function . The right graphic in the middle visualizes the resulting subset-theoretic relation for the case of sufficiency. The table on the right shows how and change as a result of altering , , or . Different outcome set scores can be generated by changing the seed.
C
C⊃O
C⊂O
C=O
O
ζ
ω
X
τ
c
μ
lin
μ
quad
μ
root
μ
log
ω
ζ
τ
c
μ
quad
μ
root