Cooling by a Cylindrical Pin Fin
Cooling by a Cylindrical Pin Fin
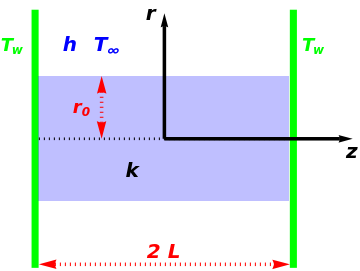
In electronic systems, a fin is a heat sink or a passive heat exchanger that cools a device by dissipating heat into the surrounding medium (e.g. air). This diagram shows a cylindrical pin fin, used to maximize heat transfer to a fluid between two walls:
The walls are at a high temperature . The fluid flowing over the pin has a free stream temperature . The heat transfer coefficient between the pin wall and the surrounding medium is labeled (in ). If one introduces the dimensionless temperature , the governing equation is:
T
w
T
∞
h
W/K
2
m
ϕ=-
T-
T
∞
T
w
T
∞
1
r
∂
∂r
∂ϕ
∂r
2
∂
∂
2
z
with and .
0≤r≤
r
0
0≤z≤L
The associated boundary conditions are then:
∂ϕ
∂z
z=0
∂ϕ
∂r
r=0
∂ϕ
∂r
h
k
r=
r
0
ϕ(z=L)==1
ϕ
w
where is the thermal conductivity of the cylindrical pin fin and =1.
k (W/m K)
r
0
The Demonstration plots the contours of the dimensionless temperature for a user-set value of the Biot number. This solution is based on Chebyshev orthogonal collocation with collocation points.
N=21
The analytical solution of the differential equation obtained by separation of variables [1] is given by:
ϕ=
∞
∑
n=1
2 ( r)cosh( z)
B
i
J
0
λ
n
λ
n
cosh( L)()+
λ
n
J
0
λ
n
r
0
2
()
λ
n
r
0
2
B
i
B
i
h
r
0
k
λ
n
f(λ)=(λ )(λ )-(λ )
r
0
J
1
r
0
J
0
r
0
B
i
We have found excellent agreement between our numerical solution and the analytical solution.