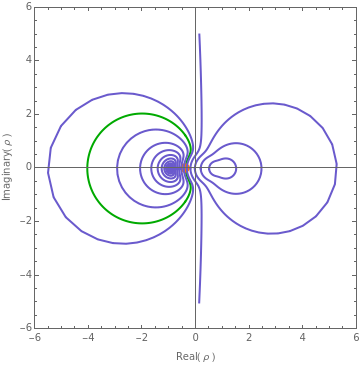
Constant Angle of Incidence Contours for an Air-SiO2-Si System
Constant Angle of Incidence Contours for an Air-SiO2-Si System
The ellipsometric function for an ambient-film-substrate system is defined as the ratio of complex-amplitude reflection coefficients for the and polarization:
ρ
r
p
s
ρ
r
Rp
R
s
A+BX+C
2
X
D+EX+F
2
X
where are functions of Fresnel interface reflection coefficients , , , and . The pairs and signify the ambient-film and film-substrate interfaces. Here is an exponential function of metric film thickness and is the thickness period. If the ambient and film media are transparent, the point representing moves uniformly in a clockwise direction around the unit circle in the complex plane as increases from 0 to . Because is related to by an analytic rational function, the point representing must trace a closed contour in the complex plane as traces the unit circle in the complex plane.
A,B,C,D,E,andF
r
01p
r
12p
r
01s
r
12s
01
12
X=exp-j2πd
D
ϕ
d
D
ϕ
X
X
d
D
ϕ
ρ
r
X
ρ
r
ρ
r
X
X
The figure shows such a family of non-intersecting, constant angle of incidence contours (CAIC) for (normal incidence) to (grazing incidence) for the system at .
ϕ=0
ϕ=90°
air--Si
SiO
2
λ=632.8nm