
You are using a browser not supported by the Wolfram Cloud
Supported browsers include recent versions of Chrome, Edge, Firefox and Safari.
I understand and wish to continue anyway »
1. | 2. |
2.2 | 3. |
4. | 10. |
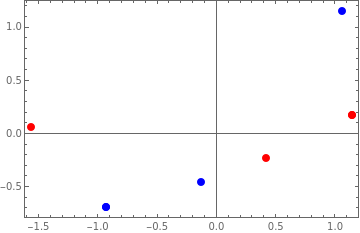
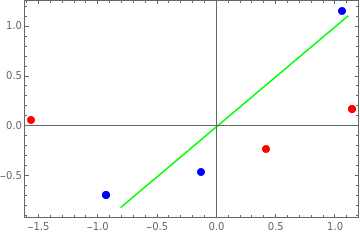
-0.927173 | -0.688247 |
-0.132453 | -0.458831 |
1.05963 | 1.14708 |

1. | 0.957186 |
0.957186 | 1. |
0.168946 | 1.14227 |
-0.230784 | 0.418101 |
0.0618385 | -1.56038 |

1.14227 | 0.168946 |
0.418101 | -0.230784 |
-1.56038 | 0.0618385 |
0.168946 | 1.14227 |
-0.230784 | 0.418101 |
0.0618385 | -1.56038 |
1. | 0. |
0. | 1. |
0.57735 | 0.57735 | 0.57735 |
0.211325 | -0.788675 | 0.57735 |
-0.788675 | 0.211325 | 0.57735 |
1.97848 | 0. |
0. | 0.292623 |
0. | 0. |
1.14227 | 0.168946 |
0.418101 | -0.230784 |
-1.56038 | 0.0618385 |
1.14227 | 0.168946 |
0.418101 | -0.230784 |
-1.56038 | 0.0618385 |

You are using a browser not supported by the Wolfram Cloud
Supported browsers include recent versions of Chrome, Edge, Firefox and Safari.
I understand and wish to continue anyway »