166 7.7 Example 9: Using the Comparison Theorem for Non-negative Integrals.
166 7.7 Example 9: Using the Comparison Theorem for Non-negative Integrals.
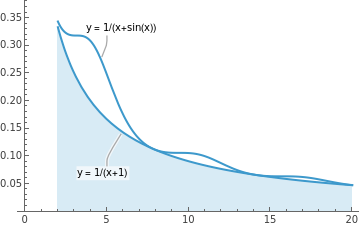
Example 9 (a) picture:
Example 9 (a) picture:
Show[Plot[Callout[1/(x+1),"y = 1/(x+1)",{5,0.1}],{x,2,20},PlotRange->{0,.35},Filling->Axis], Plot[Callout[1/(x+Sin[x]),"y = 1/(x+sin(x))",{5,0.3}],{x,2,20},PlotRange->{0,.35}]]
Out[]=
Theshadedregioncorrespondstox,whichdiverges.Sinceweknowthatforallx≥2,0≤≤,itfollowsfromtheComparisonTheoremforNon-NegativeIntegrands(Theorem1inLecture10)thatxdiverges!
∞
∫
2
1
(x+1)
1
(x+1)
1
(x+sin(x))
∞
∫
2
1
(x+sin(x))
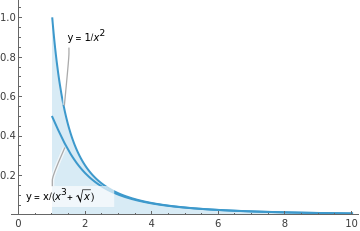
Example 9 (b):
Example 9 (b):
Picture for example 9 (b):
Picture for example 9 (b):
ShowPlotCallout1x^2,"y = 1/",{1.5,0.8},{x,1,10},Filling->Axis,PlotRange->{0,1}, PlotCalloutx(x^3+Sqrt[x]),"y = x/+
2
x
3
x
x
",{1,0.2},{x,1,10},PlotRange->{0,1}Out[]=
Theshadedregioncorrespondstox=1.Sinceweknowthatforallx≥1,0≤+≤,itfollowsfromtheComparisonTheoremforNon-NegativeIntegrands(Theorem1inLecture10)that+xconverges!
∞
∫
1
1
2
x
x
3
x
x
1
2
x
∞
∫
1
x
3
x
x
Estimate the integral in Example 9 (b):
Estimate the integral in Example 9 (b):
ObservethatI=+,where=f(x)xand=f(x)x.ItfollowsthatwecanestimateI≈.(UsetheTrapezoidRulewithn=50toestimate.)
I
1
I
2
I
1
10
∫
1
I
2
∞
∫
10
I
1
I
1
In[]:=
Trapezoid[f_,a_,b_,n_]:=(1/2)(f[a+(i-1)*(b-a)/n]+f[a+i*(b-a)/n])*(b-a)/n
n
∑
i=1
In[]:=
f[x_]:=x/(x^3+Sqrt[x])
N[Trapezoid[f,1,10,50]]
Out[]=
0.714904
Thus, ≈ 0.714904, so we can conclude that I ≈ .
I
1
I
1
Error estimate for Example 9 (b): Let I = I1+ I2 where I1=10∫1f(x)x and I2=∞∫10f(x)x.
Error estimate for Example 9 (b): Let I = + where =f(x)x and =f(x)x.
I
1
I
2
I
1
10
∫
1
I
2
∞
∫
10
NowfindanupperboundontheerrorintroducedbyusingtoestimateI.Thewaytodothisistoobservethat |I-|=|+-|=-+≤-+≤(errorinusingthetrapezoidruletoestimate)+≤(b-a)+g(x)xwhereisanupperboundon|f''(x)|n[a,b]and0≤f(x)≤g(x)forx≥10.Weneedtofindavaluefor.Thefollowingworkshowsthatwecantaketobe0.276.
I
1
T
n
I
1
I
2
T
n
I
1
T
n
I
2
I
1
T
n
I
2
I
1
I
2
3
K
2
12
2
n
∞
∫
10
K
2
K
2
K
2
NSolve[f'''[x]==0,x]
Out[]=
{{x1.47319},{x-1.19184-0.865921},{x-1.19184+0.865921},{x0.324042-0.153639},{x0.324042+0.153639},{x-0.171849-0.314763},{x-0.171849+0.314763},{x-0.352462-0.0661711},{x-0.352462+0.0661711}}
N[f''[{1,1.47319,10}]]
Out[]=
{-0.125,0.275014,0.000592229}
{-0.125`,0.275014321953694507`,0.000592229048906810007`}
Out[]=
{-0.125,0.275014,0.000592229}
If we choose to be a number larger than 0.275014321953694507, then we can estimate the error!
K
2
In[]:=
K2=0.276;
Itfollowsthataboundontheerrorinusingthetrapezoidrulewithn=50toestimate,i.e.|-|,is:
I
1
I
1
T
50
(K2*(10-1)^3)/(12*50^2)
Out[]=
0.0067068
Nowweneedtoestimatetheerrorinignoringthetail(i.e.).Takeg(x)=.
I
2
1
2
x
Limit[Integrate[1/x^2,{x,10,t}],t->Infinity]
Out[]=
1
10
Thus,|I-|≤0.0067068+0.10=0.1067068.
T
50