Inhibition of Enzyme Reactions in Continuous Stirred-Tank Reactor and Batch Reactor
Inhibition of Enzyme Reactions in Continuous Stirred-Tank Reactor and Batch Reactor
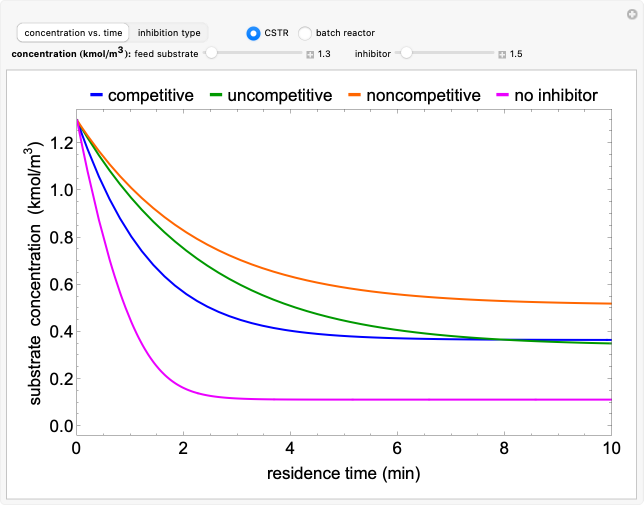
Inhibitors decrease the rates that enzymes bind to substrates and convert them to products. Three types of inhibition (competitive, uncompetitive, noncompetitive/mixed) and reaction with no inhibitor are compared for an enzyme reaction that obeys Michaelis–Menten kinetics. Substrate concentration is plotted versus time for a continuous stirred-tank reactor (CSTR) and for a batch reactor. Change the inhibitor concentration, which remains constant during reaction, with a slider. Set the substrate feed concentration with a slider. Select "inhibition type" to see the reaction steps, pathways, and a brief description of the type of inhibition. In competitive inhibition, the inhibitor attacks the enzyme to form an enzyme-inhibitor complex ; adding more substrate minimizes the inhibitor effect. In uncompetitive inhibition, the inhibitor attacks the enzyme-substrate complex ; adding more substrate does not overcome this type of inhibition since the inhibitor does not compete with the substrate for the enzyme sites. In noncompetitive inhibition, the inhibitor attacks the enzyme to form an enzyme-inhibitor complex or it attacks the enzyme-substrate complex to form an enzyme-substrate-inhibitor complex .
E·I
E·S
E·I
E·S
E·S·I
Details
Details
For a continuous-stirred tank reactor (CSTR) the material balance is written in the form of a differential equation:
C
S
t
C
S,i
C
S
r
S
for a batch reactor the material balance is:
C
S
t
r
S
where is substrate concentration (), is the feed substrate concentration (), is the rate of substrate consumption for various types of inhibition (), is residence time (min), and is time (min).
C
S
kmol/
3
m
C
S,i
kmol/
3
m
r
S
kmol/[min]
3
m
τ
t
Rate laws are different for each type of inhibition:
competitive: ,
-=+1+
r
S
V
max
C
S
C
S
K
M
C
I
K
I
uncompetitive: ,
-=+1+
r
S
V
max
C
S
K
M
C
S
C
I
K
I
noncompetitive (mixed): ,
-=
r
S
V
max
C
S
(+)1+
C
S
K
M
C
I
K
I
no inhibitor: ,
-=+
r
S
V
max
C
S
K
M
C
S
where is inhibitor concentration (), and are inhibitor and Michaelis constants (), and is the rate of reaction ().
C
I
kmol/
3
m
K
I
K
M
kmol/
3
m
V
max
kmol/[min]
3
m
References
References
[1] H. S. Fogler, Essentials of Chemical Reaction Engineering, Boston: Pearson Education, 2011 pp. 349–370.
External Links
External Links
Permanent Citation
Permanent Citation
Rachael L. Baumann, John L. Falconer
"Inhibition of Enzyme Reactions in Continuous Stirred-Tank Reactor and Batch Reactor"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/InhibitionOfEnzymeReactionsInContinuousStirredTankReactorAnd/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: April 8, 2014