Unit-Norm Vectors under Different p-Norms
Unit-Norm Vectors under Different p-Norms
This Demonstration shows how unit-norm vectors look under different -norms, which are standard norms for finite-dimensional spaces.
p
In mathematics, a norm is a function that assigns a length (or size) to a vector. The vector is an object in a vector space, and can thus be a function, matrix, sequence, and so on. A -norm is a norm on a finite-dimensional space of dimension defined as
p
N
||u=
||
p
1/p
N
∑
n=1
u
n
p
|
This Demonstration shows sets of unit-norm vectors for different -norms.
u
p
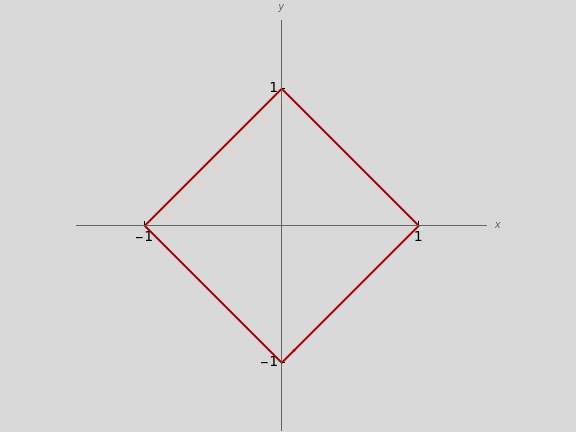
The norm for is called the Manhattan or taxicab norm because represents the driving distance from the origin to following a rectangular street grid
p=1
||u
||
1
u
||u=|x|+|y|.
||
1
The norm for is the usual Euclidean square norm obtained using the Pythagorean theorem
p=2
||u=
||
2
x+y
.2
|
2
|
The norm for is simply the maximum over and ,
p=∞
x
y
||u=max(x,y).
||
∞
Vectors ending on the red lines are of unit norm in the corresponding -norm.
p
References
References
[1] M. Vetterli, J. Kovačević, and V. K. Goyal, Foundations of Signal Processing, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2014. www.fourierandwavelets.org.
External Links
External Links
Permanent Citation
Permanent Citation
Jelena Kovacevic
"Unit-Norm Vectors under Different p-Norms"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/UnitNormVectorsUnderDifferentPNorms/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: June 18, 2012