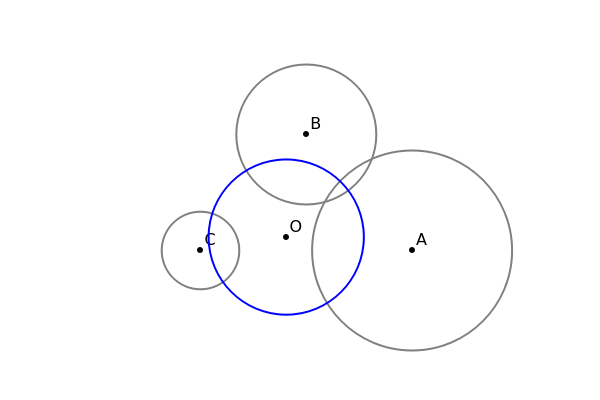
Radical Circle of Three Circles
Radical Circle of Three Circles
The radical circle of three circles has center at the radical center and is orthogonal to each of the three circles.
O
Let the centers of the circles form the triangle and let its side lengths be , , .
ABC
a=BC
b=CA
c=AB
Using Conway triangle notation, define
S
A
2
b
2
c
2
a
2
S
B
2
c
2
a
2
b
2
S
C
2
a
2
b
2
c
2
Half the triangle's area is then given by
S=2ABC
S=++
S
A
S
B
S
B
S
C
S
C
S
A
In those terms, suppose the Cartesian coordinates of three centers are at , , and the corresponding radii are , , .
A=(b,0)
B=,
S
C
b
S
b
C=(0,0)
x
y
z
Then the radical circle of the three circles , , is the circle , where
⊙(A,x)
⊙(B,y)
⊙(C,z)
⊙(O,ξ)
O=(-)+++-++,-++
2
b
2
a
S
A
2
x
S
C
2
y
S
B
2
z
S
C
2
b
S
B
2
y
2
z
S
A
2
x
S
C
2b
2
S
2
b
S
B
2
y
2
z
S
A
2
x
S
C
2bS
ξ=
4+++-2++++(+)
2
R
2
S
S
A
2
-
2
y
2
z
S
B
2
(-)
2
z
2
x
S
C
2
-
2
x
2
y
S
A
S
B
2
x
2
y
S
B
S
C
2
y
2
z
S
C
S
A
2
x
2
z
2S
Details
Details
Exercise: verify that the side lengths are indeed , , from the coordinates of the vertices.
a
b
c
External Links
External Links
Permanent Citation
Permanent Citation
Minh Trinh Xuan
"Radical Circle of Three Circles"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/RadicalCircleOfThreeCircles/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: May 10, 2022