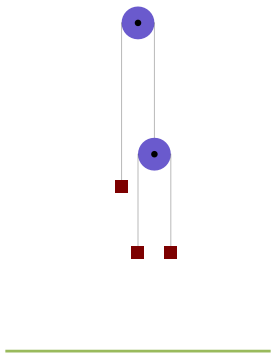
Double Atwood Machine
Double Atwood Machine
Atwood's machine consists of two masses connected by an inextensible string of negligible mass going over a pulley. A variation shown in this Demonstration replaces one of the masses by another pulley with two masses. The system now has two degrees of freedom. The problem is to calculate the acceleration of the second pulley and one of its masses. The mass on the left and the second pulley have opposite acceleration as do the masses at the center and right. Activating the time trigger will show the accelerations and distances traveled after time .
t
Details
Details
The accelerations of the pulleys are:
a
left
m
1
m
2
m
3
m
2
m
3
m
1
m
2
m
3
m
2
m
3
a
right
2(-)
m
1
m
2
m
3
4+(+)
m
2
m
3
m
1
m
2
m
3
External Links
External Links
Permanent Citation
Permanent Citation
Enrique Zeleny
"Double Atwood Machine"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/DoubleAtwoodMachine/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: October 8, 2010