Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium for an Ethanol-Water Mixture
Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium for an Ethanol-Water Mixture
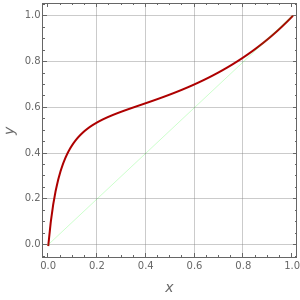
Consider a binary mixture of ethanol and water. Vapor-liquid equilibrium (VLE) data can be computed using the modified Raoult's law: , where is the vapor pressure, is the total pressure, and are the liquid and vapor phase mole fractions of the light component (i.e., ethanol) when , and finally, is the activity coefficient. You can vary the pressure to any value between and (i.e., low to moderate pressure so that the ideal gas-phase assumption holds). You can choose among five activity coefficient models (i.e., van Laar, NRTL, Wilson, Margules, or UNIQUAC). The Demonstration plots the isobaric vapor-liquid equilibrium diagram as well as the equilibrium curve. You can check that all models used to predict activity coefficients give similar results (i.e., a minimum boiling or positive azeotrope at ).
P=
y
i
sat
P
i
x
i
γ
i
sat
P
i
P
x
i
y
i
i=1
γ
P
50
200kPa
P=101.325kPa
Permanent Citation
Permanent Citation
Housam Binous, Mamdouh Al-Harthi, Brian G. Higgins
"Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium for an Ethanol-Water Mixture"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/VaporLiquidEquilibriumForAnEthanolWaterMixture/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: December 19, 2011