Atwood's Machine
Atwood's Machine
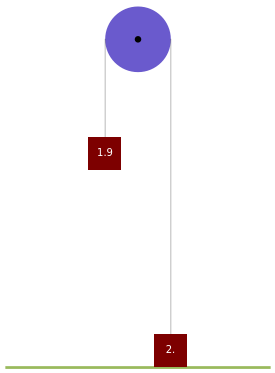
A simple demonstration of Newton's second law is provided by Atwood's machine, which consists of a pulley between two masses. The problem is to calculate the acceleration of the two masses. (Their magnitudes are equal but of opposite sign.) If the masses are equal, the system is in equilibrium and nothing moves.
Details
Details
The acceleration of the left-hand mass is given by , where and are the left- and right-hand masses in kg and is the acceleration due to gravity. It travels a distance while the trigger is active (it is stopped when the || button is clicked). The quantities and are taken as positive when the left-hand mass moves upward and negative when it moves downward. The time during which the masses are moving before hitting bottom is given by .
a=-+g
m
1
m
2
m
1
m
2
m
1
m
2
g
d
a
d
t=
2d/a
External Links
External Links
Permanent Citation
Permanent Citation
Enrique Zeleny
"Atwood's Machine"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/AtwoodsMachine/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: December 6, 2007