University of Illinois at Urbana - ChampaignDept . of Electrical and Computer Engineering
ECE 101 : Exploring Digital Information Technologies for Non-Engineers
ECE 101 : Exploring Digital Information Technologies for Non-Engineers
Lecture 9: Social Networks
9.1 Some Stats
9.
1
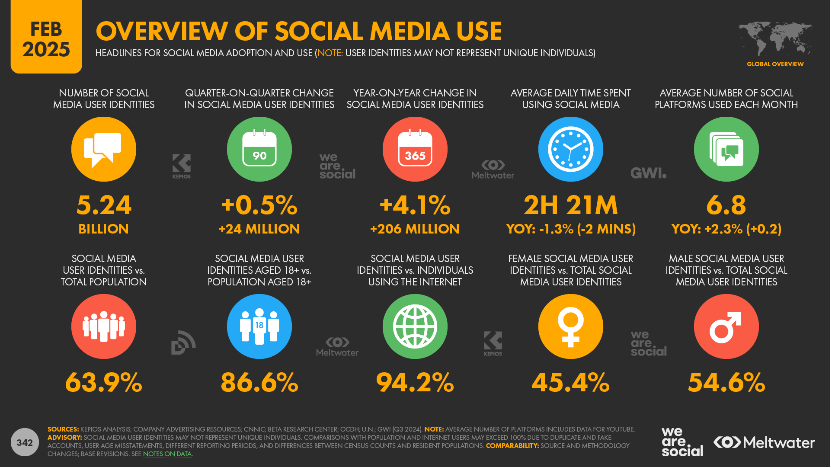
Some StatsReference: https://datareportal.com/social-media-users
9.2 Some Stats
9.
2
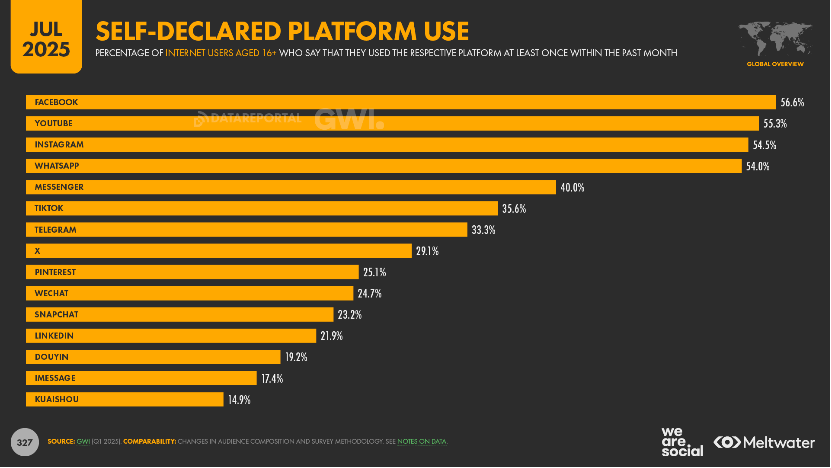
Some StatsReference: https://datareportal.com/social-media-users
9.3 What is Social Media?
9.
3
What is Social Media? ◼
Online platforms that allow users to create, share, and interact with content and each other
◼
Has become an integral part of our lives, influencing how we communicate, access information, and even perceive the world
9.4 Digital Mechanisms of Social Media
9.
4
Digital Mechanisms of Social Media◼
User Profiles and Content Creation
◼
Networking and Connectivity
◼
Algorithms and Personalization
◼
Privacy and Data Security
9.5 Social Networks on Social Media
9.
5
Social Networks on Social MediaGraph Recap
Graph Recap
A graph is a collection of objects sharing some form of relationship. These objects are referred to as vertices (or nodes) and the relationships as edges (or links).
Undirected, unweighted graph
Undirected, unweighted graph
Out[]=
Directed, unweighted graph
Directed, unweighted graph
Out[]=
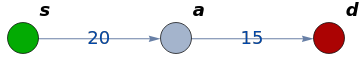
Undirected, weighted graph
Undirected, weighted graph
Out[]=
Directed, weighted graph
Directed, weighted graph
Out[]=
Graph v.s Network
Graph v.s Network
Examples of Networks
Examples of Networks
9.6 Social Networks represented by Graphs
9.
6
Social Networks represented by GraphsGraphs can be used to represent social networks
◼
Vertices are people
◼
Edges are relationships
In[]:=
ExampleData[{"NetworkGraph","FamilyGathering"},"LongDescription"]
In[]:=
fg=ExampleData[{"NetworkGraph","FamilyGathering"}]
9.7 Graph Properties
9.
7
Graph PropertiesGraphs have properties that convey useful information.
In[]:=
fg
Number of vertices (number of people in this family):
In[]:=
VertexCount[fg]
Number of edges (number of distinct relationships):
In[]:=
EdgeCount[fg]
List all the vertices (members of the family):
In[]:=
VertexList[fg]
List all the edges (the relationships):
In[]:=
EdgeList[fg]
In[]:=
fg
The vertex degree for a vertex is the number of edges incident to .
List the number of edges incident to each vertex:
v
v
List the number of edges incident to each vertex:
In[]:=
VertexDegree[fg]
In[]:=
VertexList[fg]
Number of edges associated with a particular vertex:
In[]:=
VertexDegree[fg,"Anna"]
In[]:=
VertexDegree[fg,"Oscar"]
Find the set of vertices with maximum vertex degree:
In[]:=
GraphHub[fg]
In[]:=
fg
The greatest distance between any pair of vertices:
In[]:=
GraphDiameter[fg]
Shortest path between two vertices:
In[]:=
GraphDistance[fg,"James","Felicia"]
In[]:=
FindShortestPath[fg,"James","Felicia"]
In[]:=
GraphDistance[fg,"Felicia","Rudy"]
In[]:=
FindShortestPath[fg,"Felicia","Rudy"]
Cliques are special graphs. Each vertex is connected to every other vertex.
In[]:=
c=FindClique[fg]
In[]:=
fg
In[]:=
HighlightGraph[fg,Subgraph[fg,c]]
9.8 Small World Graph
9.
8
Small World GraphHuman relationships—the social graph—form a type of graph now called a small-world graph, named after the expression, “It’s a small world!”
Small world graphs have certain properties:
◼
small diameter and typical path length,
◼
local cliques,
◼
densely connected,
◼
heavy tail
Small Diameter
Small Diameter
Is our family graph an example of a small world graph?
Is our family graph an example of a small world graph?
Six Degrees of Separation
Six Degrees of Separation
Popular ideas about six degrees of separation:
The Experiment
The Experiment
Should we play the game “Six Degrees of Kevin Bacon”? (If there is time)
Should we play the game “Six Degrees of Kevin Bacon”? (If there is time)
Social networks inherit properties of small world graphs and capture human relationship
◼
local cliques (a person’s friends tend to know one another)
◼
densely connected (most of the people have lots of connections)
◼
heavy tails (some nodes have very high degree--the influencers--while other nodes have a reasonable number of connections)
Two pillars of digital technologies as discussed in this course: Information and Computation
Communities
Communities
Graph Mining
Graph Mining
Your turn ... Class Participation Question
Your turn ... Class Participation Question
How do companies store and provide access to a social graph?
In case you are interested about this picture
In case you are interested about this picture
Each Node and Associated Edges Map into One Piece
Each Node and Associated Edges Map into One Piece
Full Copy of Graph in Each of a Few Datacenters
Full Copy of Graph in Each of a Few Datacenters
Datacenters Provide Data Fast at Expense of Consistency
Datacenters Provide Data Fast at Expense of Consistency
◼
Algorithms analyze user behavior to curate personalized content feeds.
◼
Collect information about your interactions and preferences
◼
track various interactions such as likes, comments, shares, and time spent on posts
◼
monitor how users engage with different types of content (e.g., videos, photos, articles) and which formats keep users engaged longer.
◼
consider your search queries and the profiles or pages you visit.
◼
data from your device and location to tailor content relevant to your geographical area
◼
Personalization: Based on the collected data, algorithms rank content to prioritize what appears at the top of your feed.
◼
Recommendations: Suggest new content, profiles, or pages to follow based on your interests and the behavior of similar users.
◼
Targeted ads: Based on your interactions and preferences. E.g., if you frequently engage with fitness content, you might see ads for workout gear or health supplements.
Fake News Travels the Network
Fake News Travels the Network
Impact on communication
Impact on communication
Mental health
Mental health
Influencers on Social Networks command undue “Influence”
Influencers on Social Networks command undue “Influence”
◼
Graph vs. Network
◼
Social network represented as a graph
◼
Properties of a small world graph
◼
Properties of social network that make it a small world graph
◼
vertices (or nodes) and edges (or links)
◼
Vertex degree, graph diameter, graph hub, shortest path
◼
Applications of computing on social network: Communities and Shopping Recommendations
◼
Issues with storing a large network graph and solutions; TAO
◼
Machine Learning for personalization and recommendations
◼
How algorithms shape what you see on social media from the Today show
◼
◼
American's Social Media Use by the Pew Research Center
◼
Analyzing the Social Web by Jennifer Golbeck