Electrical Conductivity of Silicon Semiconductors
Electrical Conductivity of Silicon Semiconductors
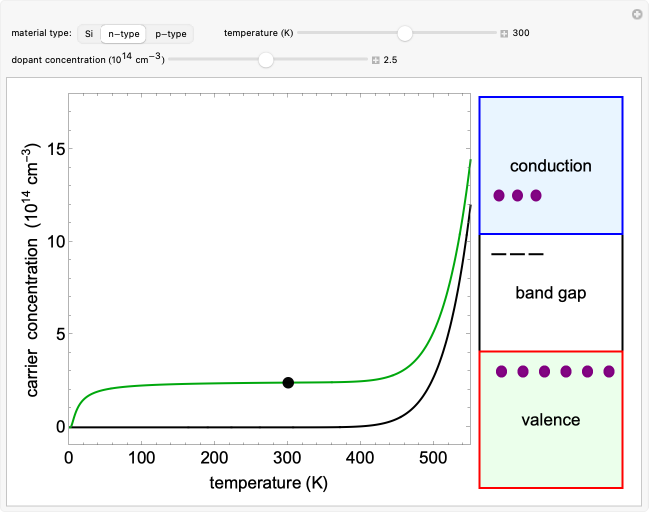
This Demonstration shows the charge carrier concentration in silicon (Si) and doped Si (n- and p-types) as a function of temperature and dopant concentration. The corresponding electron band configurations are shown to the right of the plot. Phosphorous doping creates n-type Si, while boron doping creates p-type Si.
Details
Details
The intrinsic carrier concentration () is:
C
i
C
i
-
E
g
2T
k
B
e
N=
N
0
2.54
(T/300)
where is the effective density of states (), is the energy gap (eV), is Boltzmann's constant (eV/K), is temperature (K), and is the effective density of states at 300 K.
N
-3
cm
E
g
k
B
T
N
0
The carrier concentration for pure silicon () is:
C
Si
C
Si
19
10
2.54
(T/300)
-6729/T
e
The carrier concentration for doped silicon () is:
C
Si,dop
C
Si,dop
C
Si
C
dop
-E/R/T
e
where is the atomic concentration of dopant atoms, is the activation energy for the electron of a dopant atom, and is the ideal gas constant.
C
dop
E
R
All carrier concentration are in units of .
-3
cm
External Links
External Links
Permanent Citation
Permanent Citation
Nathan S Nelson, Rachael L. Baumann, John L. Falconer
"Electrical Conductivity of Silicon Semiconductors"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/ElectricalConductivityOfSiliconSemiconductors/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: September 21, 2015