Rational Pedal-Antipedal Triangles
Rational Pedal-Antipedal Triangles
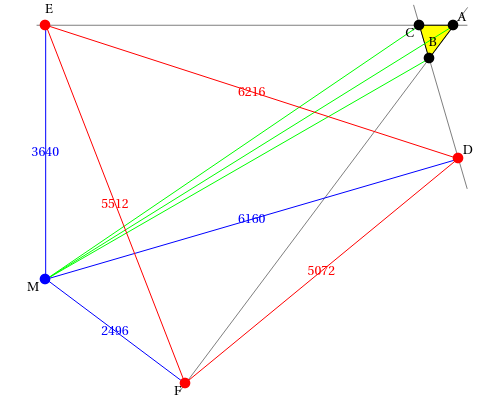
In a rational polygon, the distance between any two vertices is a rational number.
Let be the pedal triangle or the antipedal triangle of any point with respect to the triangle .
DEF
M
ABC
A theorem states that is a rational quadrilateral if and only if is a rational quadrilateral.
MABC
MDEF
In this Demonstration, rational values , , , and are used to generate a pair of rational pedal-antipedal triangles and that correspond to the rational point .
x
y
z
u
v
ABC
DEF
M
External Links
External Links
Permanent Citation
Permanent Citation
Minh Trinh Xuan
"Rational Pedal-Antipedal Triangles"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/RationalPedalAntipedalTriangles/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: March 17, 2023