Geometric Brownian Motion with Nonuniform Time Grid
Geometric Brownian Motion with Nonuniform Time Grid
This Demonstration simulates geometric Brownian motion (GBM) paths with a nonuniform time grid. A GBM is a continuous-time stochastic process in which the logarithm of the randomly varying quantity follows a Brownian motion (also called a Wiener process) with drift. In computational finance, GBM is used to model stock prices in the Black–Scholes model and is the most widely used model of stock price behavior.
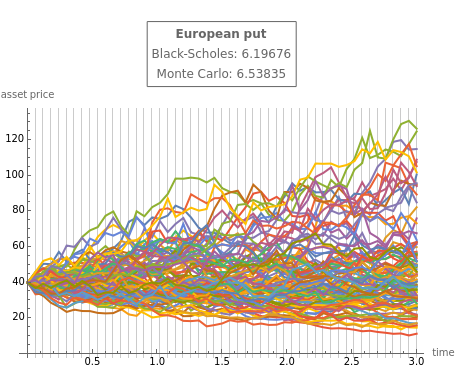
As an example, this Demonstration generates random GBM paths and uses Monte Carlo simulation to estimate the price of a European put option, with starting stock price , strike price , maturity time , stock price volatility , risk-free interest rate , and stock dividend yield . The simulation output is compared against the analytic Black–Scholes output, calculated with Mathematica's built-in function FinancialDerivative.
S
0
X
T
σ
r
δ
The coefficient () generates nonuniform time steps with decreasing length as we approach maturity, according to the model: =h·. If , the time grid becomes uniform.
h
0<h≤1
dt
i
dt
i-1
h=1
Details
Details
Let denote the number of time steps and the number of GBM paths. The list of the stock prices that the GBM path consists of are generated according to the following process:
n
m
n+1
th
k
S
k,i
S
k,i-1
dt
i-1
dt
i-1
i=2,3,…,n+1
S
k,1
S
0
Z
μ=r-δ-
2
σ
2
The Monte Carlo estimation of the European put option derives from the discounted average of the option's possible payoffs at expiry:
-r·T
e
m
m
∑
j=1
S
j,n+1
This Demonstration does not use Mathematica's built-in function GeometricBrownianMotionProcess because the Monte Carlo simulation using RandomFunction requires fixed time steps as in RandomFunction[GeometricBrownianMotionProcess[mu,sigma,x0],{t0,tend,dt}].
dt
External Links
External Links
Permanent Citation
Permanent Citation
Michail Bozoudis, Michail Boutsikas
"Geometric Brownian Motion with Nonuniform Time Grid"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/GeometricBrownianMotionWithNonuniformTimeGrid/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: June 20, 2016