Sum of Sines
Sum of Sines
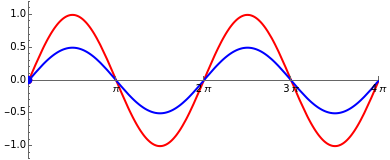
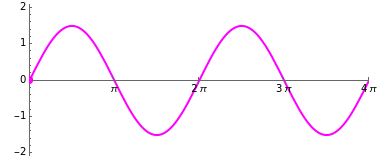
The sum of two sine waves with the same frequency is again a sine wave with frequency . This is used for the analysis of linear electrical networks excited by sinusoidal sources with the frequency . In such a network all voltages and currents are sinusoidal. The addition of sine waves is very simple if their complex representation is used.
f
0
f
0
f
0
aexp(i(ωt+ϕ))
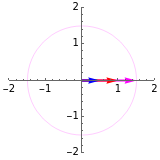
This Demonstration shows the sum of two sine waves with amplitudes , and phases , , respectively. The complex representation , as vectors in the complex plane, is shown in the left graphics column. The sine function is the imaginary part of the vector, indicated by the projection onto the imaginary axis.
a
1
a
2
ϕ
1
ϕ
2
aexp(i(ωt+ϕ))
External Links
External Links
Permanent Citation
Permanent Citation
Carsten Roppel
"Sum of Sines"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/SumOfSines/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: December 1, 2011