An Angle Invariant for Arbitrary Triangles
An Angle Invariant for Arbitrary Triangles
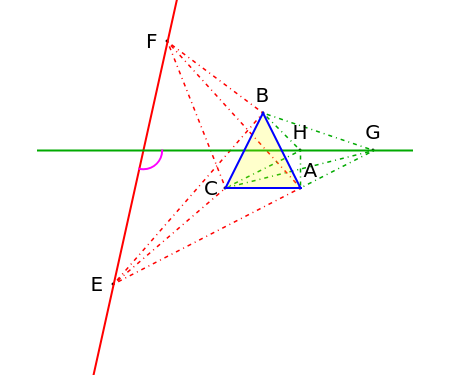
Let be the angle between two arbitrary lines and . Let be an arbitrary triangle.
ϕ
EF
GH
ΔABC
Define values relating to quadrilaterals based on the line :
EF
x=+--
2
EB
2
FC
2
EC
2
FB
y=+--
2
EC
2
FA
2
EA
2
FC
z=+--
2
EA
2
FB
2
EB
2
FA
Define values relating to quadrilaterals based on the line :
GH
u=+--
2
GB
2
HC
2
GC
2
HB
v=+--
2
GC
2
HA
2
GA
2
HC
w=+--
2
GA
2
HB
2
GB
2
HA
Then:
cosϕ=±xu+yv+zw
S
A
S
B
S
C
++++
S
A
2
x
S
B
2
y
S
C
2
z
S
A
2
u
S
B
2
v
S
C
2
w
where , , are Conway notation for the triangle .
S
A
S
B
S
C
ABC
You can drag the points.
Permanent Citation
Permanent Citation
Minh Trinh Xuan
"An Angle Invariant for Arbitrary Triangles"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/AnAngleInvariantForArbitraryTriangles/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: May 16, 2022