Bound-State Spectra for Two Delta Function Potentials
Bound-State Spectra for Two Delta Function Potentials
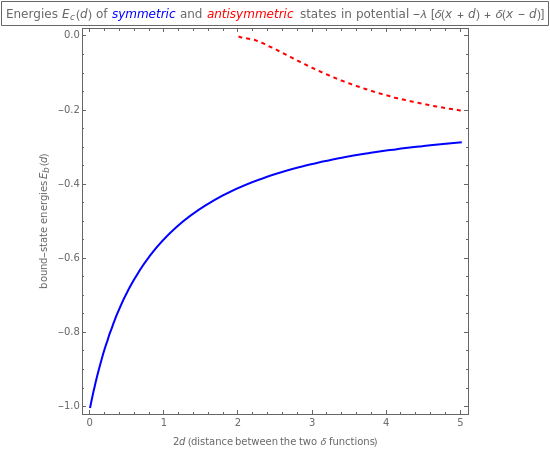
This Demonstration shows the bound-state spectra (d)of a particle of mass in the presence of two attractive potentials separated by a distance , . Since the Fourier transform of this potential is factorizable, , the bound-state spectra are easily obtained using the momentum-space Schrödinger equation. The energies are normalized to the magnitude of the symmetric-state energy at . Note that the second (antisymmetric) bound state appears only when the distance between the functions exceeds the critical value =2/λm.
E
b
m
δ
2d
V(x)=-λ[δ(x+d)+δ(x-d)]
V(k-k')=-2λcos((k-k')a)=-2λ[cos(ka)cos(k'a)+sin(ka)sin(k'a)]
d=0
δ
D
c
2
ℏ
Details
Details
Snapshot 1: typical symmetric and antisymmetric bound-state energies (d) as a function of distance between the two attractive functions
E
b
2d
δ
Snapshot 2: for a weak potential strength , a second bound-state, the antisymmetric state, appears only when the distance between the two functions is large,
λ<<1
δ
2d>>1
Snapshot 3: for a strong potential , the symmetric and antisymmetric states become degenerate when the distance between the two functions is increased
λ>>1
2d
δ
Analytical and numerical treatment of the Schrodinger equation in momentum space can be found in W. A. Karr, C. R. Jamell, and Y. N. Joglekar, "Numerical Approach to Schrodinger Equation in Momentum Space," arXiv, 2009.
External Links
External Links
Permanent Citation
Permanent Citation
Christopher R. Jamell, Yogesh N. Joglekar
"Bound-State Spectra for Two Delta Function Potentials"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/BoundStateSpectraForTwoDeltaFunctionPotentials/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: March 7, 2011