24a. Construct a Triangle Given the Length of the Altitude to the Base, the Difference of Base Angles and the Sum of the Lengths of the Other Sides
24a. Construct a Triangle Given the Length of the Altitude to the Base, the Difference of Base Angles and the Sum of the Lengths of the Other Sides
This Demonstration shows a marked-ruler (or verging) construction of a triangle given the length of the altitude to the base, the difference of angles at the base and the sum of the lengths of the other two sides.
ABC
h
C
δ
s
Construction
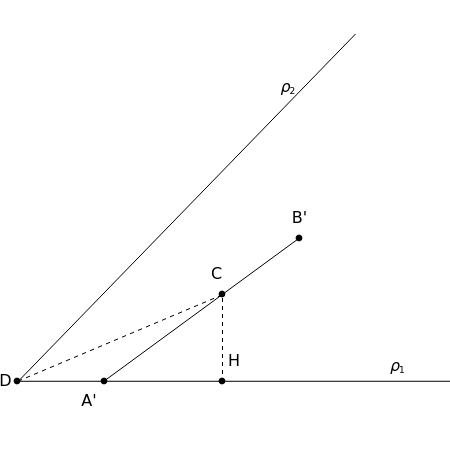
From a point draw two rays and at an angle .
D
ρ
1
ρ
2
δ
Let be on such that . Let be the intersection of the angle bisector of the angle and the perpendicular to at . Thus and is a right triangle with hypotenuse .
H
ρ
1
HD=h
C
ρ
1
ρ
2
ρ
1
H
∠CDH=δ/2
DHC
DC
Draw the line segment of length with between and and on .
A'B'
s
C
A'
B'
A'
ρ
1
Move along until is on ; call this point . Then set .
A'
ρ
1
B'
ρ
2
F
A=A'
Let be the reflection of in .
B
A
DC
Then satisfies the stated conditions.
ABC
Proof
In the triangle , , , but the exterior angle , so .
DAF
∠FDA=δ
∠AFD=β
∠FAB=α
δ=α-β
Triangles and are congruent, so , and .
DCF
DCB
CB=CF
BC+CA=a+b
Details
Details
This is a verging, or marked-ruler construction. For verging, see [1, p. 124].
References
References
[1] G. E. Martin, Geometric Constructions, New York: Springer, 1998.
External Links
External Links
Permanent Citation
Permanent Citation
Izidor Hafner
"24a. Construct a Triangle Given the Length of the Altitude to the Base, the Difference of Base Angles and the Sum of the Lengths of the Other Sides" from the Wolfram Demonstrations Project http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/24aConstructATriangleGivenTheLengthOfTheAltitudeToTheBaseThe/
Published: October 12, 2017