pH Buffering in Human Blood
pH Buffering in Human Blood
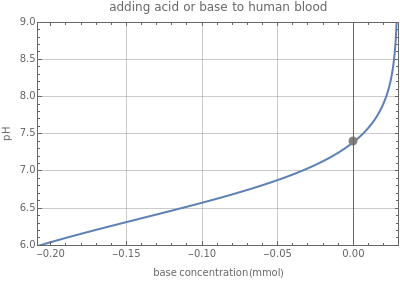
This Demonstration simulates the buffer system in human blood, showing its resistance to a change in pH by the addition of acid or base. Human blood contains carbonic acid and bicarbonate anion , which form a buffer to maintain blood pH between 7.35 and 7.45.
H
2
CO
3
-
HCO
3
Move the sliders to control the acid or base added to the buffer system. The pH is calculated using the Henderson–Hasselbalch equation: . The pH is plotted as a function of concentration. The smiley face changes according to the pH value: it smiles only when the pH is within the healthy range. A yellow sad face means that the person is experiencing acidosis; a blue sad face means alkalosis.
pH=()+log[][]
pK
a
H
2
CO
3
-
HCO
3
H
2
CO
3
Details
Details
[2] Wikipedia. "Bicarbonate Buffer System." (Nov 24, 2021) en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bicarbonate_buffer_system.
[3] Khan Academy. "Chemistry of Buffers and Buffers in Our Blood." (Nov 24, 2021) www.khanacademy.org/test-prep/mcat/chemical-processes/acid-base-equilibria/a/chemistry-of-buffers-and-buffers-in-blood.
Permanent Citation
Permanent Citation
Claire Chen, Hongdi Wu, Dalia Hassan, Yifan Lai, Kristina M. Lenn
"pH Buffering in Human Blood"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/PHBufferingInHumanBlood/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: December 17, 2021