Basic Parameters of the Spieker Center
Basic Parameters of the Spieker Center
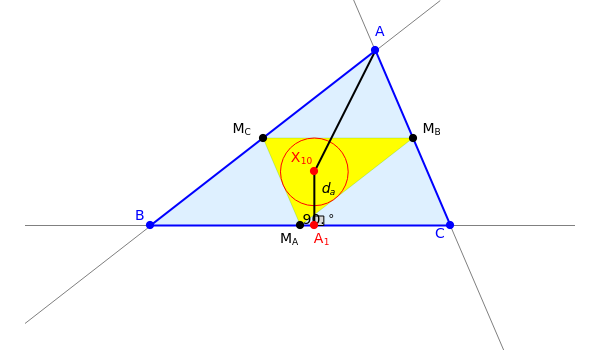
The Spieker center of a triangle is the incenter of the medial triangle of [1]. It is also the center of the excircles's radical circle.
X
10
ABC
ABC
Let , , be the exact trilinear coordinates of with respect to and =++, let , , be the side lengths opposite the corresponding vertices and let , , be the circumradius, inradius and semiperimeter of .
d
a
d
b
d
c
X
10
ABC
d
X
10
d
a
d
b
d
c
a
b
c
R
r
s
ABC
M
A
M
B
M
C
BC
CA
AB
A
1
B
1
C
1
X
10
Then
=
AX
10
-4+4sa+-3-16Rr
2
a
2
s
2
r
2
d
a
r(2s-a)
2a
d
X
10
2
s
2
r
4R
You can drag the vertices , and .
A
B
C
Details
Details
A triangle center is said to be even when its barycentric coordinates can be expressed as a function of three variables , , that all occur with even exponents. If the center of a triangle has constant barycentric coordinates, it is called a neutral center (the centroid is the only neutral center). A triangle center is said to be odd if it is neither even nor neutral.
a
b
c
X
2
Standard barycentric coordinates of a point with respect to a reference triangle are normalized to have a sum of 1.
References
References
[1] C. Kimberling. "Encyclopedia of Triangle Centers." (Aug 9, 2022) faculty.evansville.edu/ck6/encyclopedia.
External Links
External Links
Permanent Citation
Permanent Citation
Minh Trinh Xuan
"Basic Parameters of the Spieker Center"
http://demonstrations.wolfram.com/BasicParametersOfTheSpiekerCenter/
Wolfram Demonstrations Project
Published: August 11, 2022