Simulating Vehicle Suspension with a Simplified Quarter-Car Model
Simulating Vehicle Suspension with a Simplified Quarter-Car Model
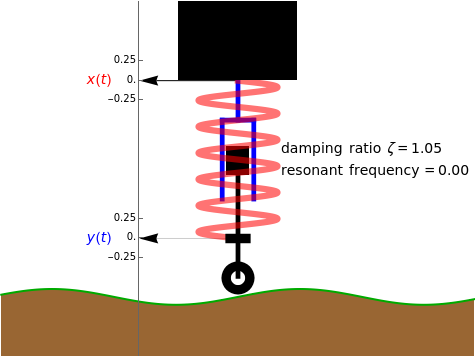
The simplified quarter-car suspension model is basically a mass-spring-damper system with the car serving as the mass, the suspension coil as the spring, and the shock absorber as the damper.
This Demonstration lets you explore the affect of different suspension parameters and road conditions on the vertical motion of the car.
The mathematics of the system are based on the differential equation of the spring-damper suspension: , which, after a Laplace transform, results in the transfer function .The Mathematica 8 functions TransferFunctionModel and OutputResponse were used to calculate the car movement with no need to solve the differential equation.
ctx'-cty'+ktx-kty+mtx''0
G(s)=
cs+k
cs+k+m
2
s
Details
Details
Snapshot 1: very hard suspension with a light car gives excessive shaking
Snapshot 2: the damping ratio is 1 and gives optimal comfort
Snapshot 3: at resonant frequency, a maximum car movement is obtained
External Links
External Links
Permanent Citation
Permanent Citation